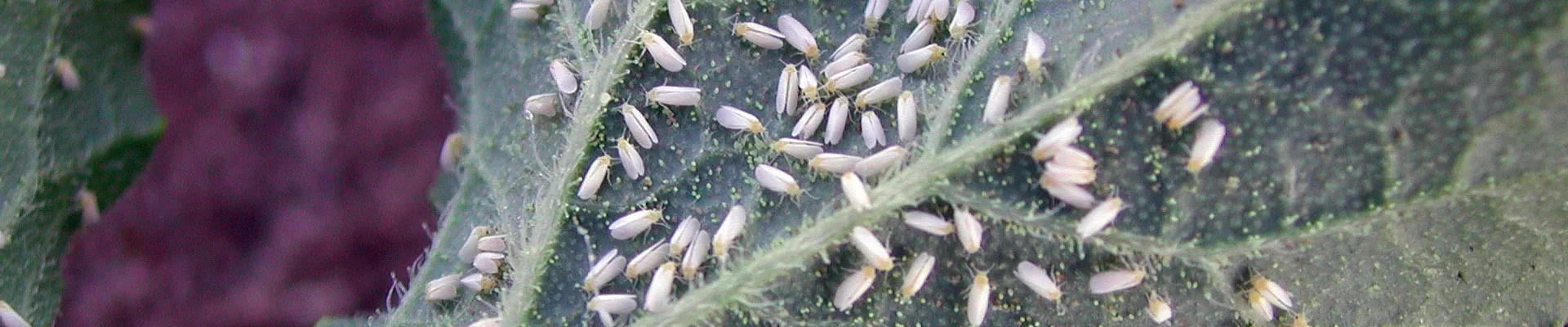
The two species of whitefly that affect many crops are Bemisia tabaci or tobacco whitefly and Trialeurodes vaporariorum or glasshouse whitefly. The main morphological difference that enables these insects to be distinguished from one another is the position of the wings. In B. tabaci, they are joined to the body and in T. vaporariorum they are parallel to the surface of the leaf. Furthermore, the adult and pupa of T. vaporariorum usually has a greater quantity of waxy powder than B. tabaci.
About the pest in brief
- What are Whiteflies?
- Whiteflies are hemipterous insects belonging to the Aleyrodidae family. They can cause considerable damage and loss of production.
- What can you see?
- Discolored patches on the parts of the leaf where the insects have been feeding.
- What can you do?
- One of the main objectives when controlling whitefly is to prevent the crop being infected by a virus that the insects can be carrying.
Biological cycle of Whitefly
The full life cycle of the whitefly lasts between 15 and 40 days, depending on environmental conditions, particularly the temperature, since eggs will develop into adults more quickly when the temperature is higher. The whitefly usually lays its eggs on the underside of the leaves, which the eggs stick to.

Symptoms of the pest
The direct damage is caused to the plant when the whitefly feeds. The sucking of the sap causes discolored patches on the parts of the leaf where they have been feeding. Furthermore, as they suck out the sap, they release toxic substances into the phloem, which then spreads throughout the plant. This leads to metabolic imbalances in the plant and general weakening, chlorosis and changes to the flowers and fruit. In terms of indirect damage, the molasses excreted by the nymphs enables fungi, such as sooty mold (Capnodium sp.), to form on the leaves. This mold acts as a screen and reduces the photosynthetic capacity of the plant.
However, the most serious damage that the whitefly can cause to crops is the transmission of viruses.
How to prevent the pest?
One of the main objectives when controlling whitefly is to avoid the crop being infected by any virus that the insects may be carrying. It is therefore important that, any weeds or remains of other plants, near the crop are removed because these can act as a habitat for whitefly. Furthermore, if a whitefly feeds off a weed that has a virus and then reaches your crop, the virus can easily spread. The use of protective barriers such as nets and covers are also a good option for preventing infestations.

Solutions for controlling the pest
A range of entomophagus insects, parasites, and some entomopathogenic fungi can be used to control whitefly. Most predators feed on the eggs and nymphs of the whitefly. This category includes the Delphastus catalinae beetle. The chrysopidae larva and some bedbugs are also good natural controllers of this pest. The small wasps of the Aphelinae family are parasites of the whitefly larvae. The wasps lay their eggs on the larvae and they develop by feeding on their host.